Cyberattacks have become one of the biggest threats in today’s digital world. Hackers exploit vulnerabilities to disrupt businesses, steal sensitive data, and cause financial losses. From phishing scams to denial-of-service (DoS) attacks, these threats impact individuals and organizations globally.

In this blog, we will explore some of the most common cyberattacks, along with real-world cases that highlight their devastating effects.
Table of Contents
Denial of Service (DoS) Attack
A Denial of Service (DoS) attack overwhelms a system or network by flooding it with excessive traffic, making it unavailable to users.
In October 2020, Amazon Web Services (AWS), which powers major websites and apps, suffered a massive outage. Hackers launched a DoS attack by sending billions of malicious requests, disrupting services like Netflix, PayPal, and Amazon. The attack led to millions in revenue loss and highlighted the vulnerabilities in cloud services.
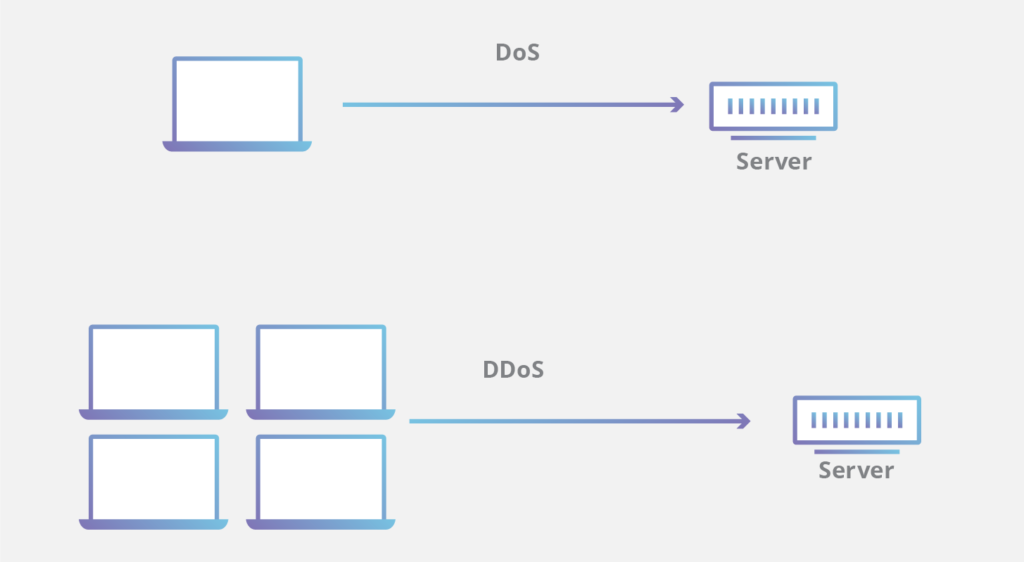
Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) Attack
A DDoS attack is a more powerful version of DoS, where hackers use multiple compromised devices (botnets) to flood a target server.
In October 2016, a massive DDoS attack hit Dyn, a company that manages internet infrastructure. Hackers used the Mirai botnet, consisting of infected IoT devices, to take down major websites like Twitter, Reddit, and Spotify. This attack proved how insecure IoT devices could be hijacked for large-scale cyber warfare.
Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) Attack
A Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) attack occurs when a hacker secretly intercepts and alters communication between two parties.
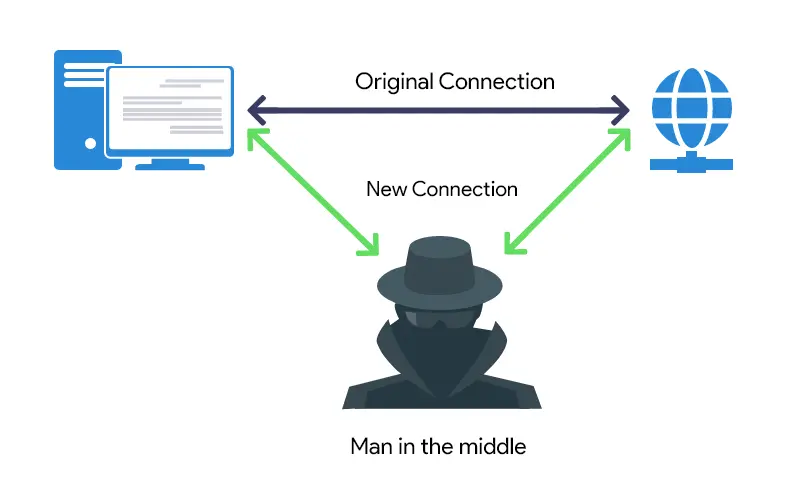
In 2013, whistleblower Edward Snowden revealed that the NSA was secretly intercepting data from companies like Google and Facebook through a MitM attack. The agency spied on millions of users worldwide by collecting sensitive information without their knowledge. This raised global concerns about privacy and government surveillance.
Phishing Attack
Phishing involves tricking users into revealing personal information, like passwords or credit card details, through fake emails or websites.
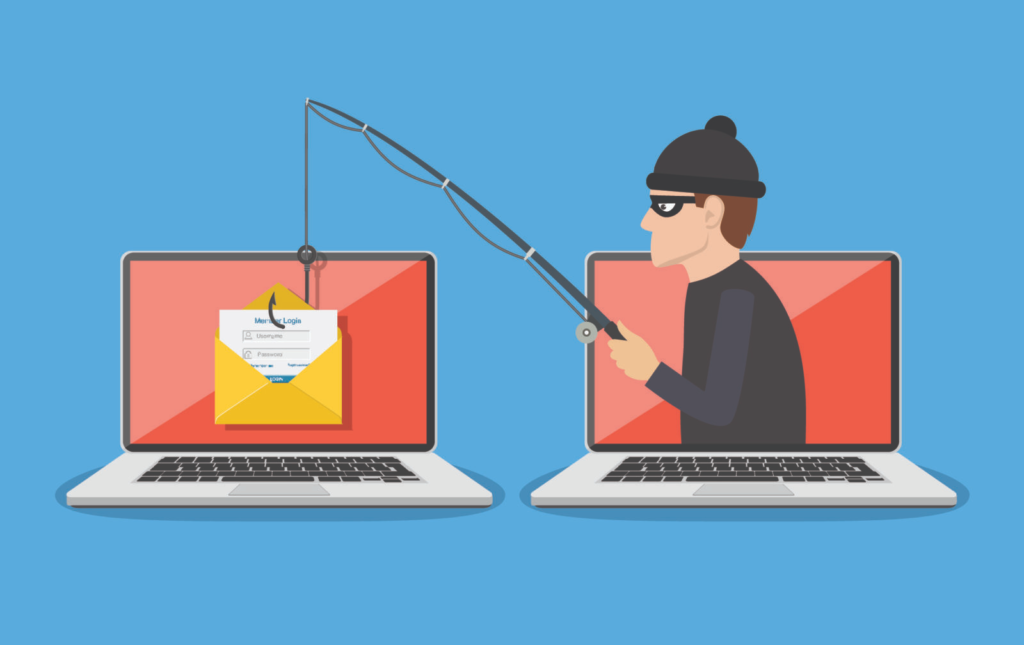

During the 2016 U.S. elections, Russian hackers launched a phishing attack on the Democratic National Committee (DNC). They sent fake emails that tricked officials into giving away login credentials. This allowed hackers to leak confidential campaign emails, affecting the election outcome and raising cybersecurity concerns.
Spoofing Attack

Spoofing is when attackers disguise themselves as trusted sources to manipulate victims.
In 2016, North Korean hackers used a spoofing attack to steal $81 million from Bangladesh’s central bank. They impersonated legitimate banking officials and sent fraudulent transactions through the SWIFT network, a global financial messaging system. This remains one of the biggest cyber thefts in history.
Spam Attack
Spam attacks involve sending mass fraudulent emails to scam people into sharing sensitive information.

One of the most infamous spam attacks is the Nigerian Prince Scam. Fraudsters send emails claiming to be a rich prince needing help to transfer money. Victims who fall for it end up losing thousands of dollars. This scam has been around since the early 2000s but still traps many unsuspecting users.
Birthday Attack
A Birthday attack exploits cryptographic hash functions by finding two different inputs that produce the same hash value, making encryption unreliable.

In 2008, researchers demonstrated a birthday attack against the MD5 hashing algorithm, which was used in SSL certificates. They showed how two different certificates could have the same hash, making it easy for hackers to forge certificates and impersonate secure websites. This led to the industry abandoning MD5 for stronger encryption.
Drive-By Attack
A drive-by attack happens when a user visits a compromised website, and malware is automatically downloaded without their knowledge.

Between 2014 and 2016, hackers injected malware into online ads on popular websites like Yahoo, The New York Times, and BBC. When users visited these sites, the ads automatically installed malware on their devices. This attack infected millions of users without them clicking on anything.

Cyberattacks are becoming more sophisticated and widespread, affecting both individuals and organizations. The cases above show how these attacks cause financial losses, data breaches, and global crises.

In Part 2, we’ll explore more advanced cyber threats like password attacks, SQL injection, malware, and social engineering, along with real-world cases.
Stay tuned for Part 2! In the meantime, ensure you:
Use strong, unique passwords
Enable two-factor authentication
Avoid clicking on suspicious links
Keep your software updated
