It’s all thanks to facial recognition technology, and one of the most advanced systems behind it is DeepFace. DeepFace was developed by Facebook and is changing the way we think about facial recognition. Let’s explore what makes DeepFace so special and how it works.
Table of Contents
What is Deep Face?
DeepFace is a facial recognition system developed by Facebook’s research team, which uses a nine-layer neural network with over 120 million connection weights. It was trained on a massive dataset of four million images uploaded by Facebook users. DeepFace is designed to analyze human faces and match them to the correct identity.
One of its most impressive features is its accuracy rate of 97.35% ± 0.25% on the Labeled Faces in the Wild (LFW) dataset, which is comparable to human-level recognition. In some cases, DeepFace even outperforms humans. However, despite its success, Facebook (now Meta) announced plans to shut down its facial recognition system due to privacy concerns. By December 2021, the company planned to delete over one billion facial recognition templates, though DeepFace itself would remain intact.
How Deep Face Began
DeepFace was developed by a team of scientists from Facebook’s AI research division. Key figures include Yainiv Taigman and Ming Yang from Facebook, along with Lior Wolf from Tel Aviv University. Taigman joined Facebook after the company acquired Face.com in 2012, which laid the groundwork for DeepFace.
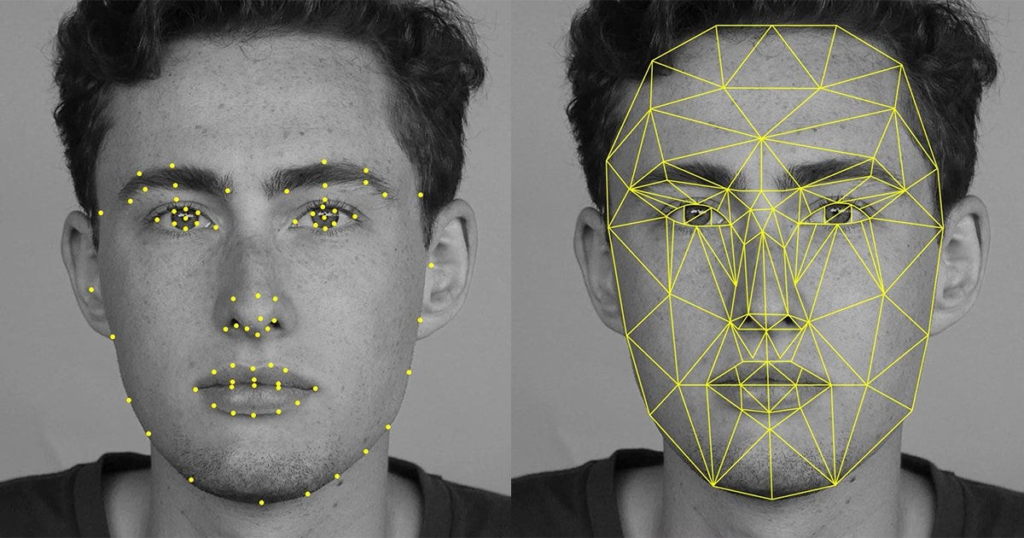
Facebook rolled out DeepFace to users in early 2015. It was designed to help people tag photos more easily and efficiently, with the goal of not invading privacy. The technology alerts users when their face appears in photos, giving them the option to remove themselves from the image if they wish.
Privacy and Concerns in Facial Recognition Technology
At first, Facebook allowed users to opt out of DeepFace. However, the company didn’t notify users that the technology was enabled, which caused concern, especially in the European Union. According to EU data protection laws, Facebook’s facial recognition system didn’t comply because users weren’t fully informed and didn’t consent to how their biometric data would be used.

As a result, DeepFace was never deployed in the EU. The legal challenges around privacy were a significant factor in Facebook’s decision to shut down its facial recognition system in 2021, though DeepFace itself wasn’t eliminated.
How DeepFace is Used
Facebook uses facial recognition templates to identify when a user’s face appears in photos across the platform. This allows users to quickly tag themselves and others. Beyond this, DeepFace helps protect people from identity theft and impersonation. For example, if someone uses another person’s profile photo, DeepFace can detect this and alert the rightful owner.

Facebook also gives users control over their facial recognition data. If someone deletes their account or untags themselves from a photo, their facial templates are also deleted from the system. If a user prefers not to be identified using facial recognition, they can disable this feature at any time.
The Impact of DeepFace’s Data
Because Facebook has the largest facial recognition dataset in the world, concerns have been raised about the potential for its distribution to government agencies. Some argue that this could violate data privacy laws, but Facebook has committed to not sharing this data with authorities.

In 2019, to address privacy concerns, Facebook removed the automatic facial recognition feature, giving users the option to opt into tagging through DeepFace.
While Facebook has taken steps to address privacy concerns, the future of DeepFace remains uncertain. Facial recognition technology will continue to evolve, and its applications could expand beyond social media. However, the shift towards greater privacy and user control will shape how companies use and implement these technologies in the years to come.
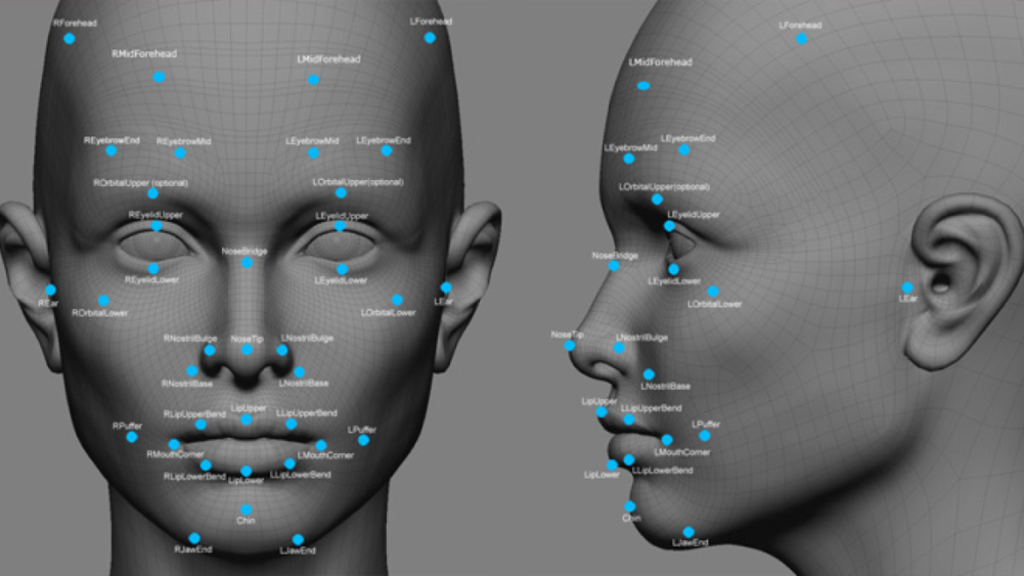
DeepFace is one of the most advanced facial recognition systems, with its high accuracy and broad applications. While privacy concerns and legal challenges have led to its shutdown in some regions, DeepFace’s technology remains a major milestone in AI development. As the conversation about privacy continues, the future of facial recognition will depend on how companies balance innovation with ethical considerations.
